 In the fast-paced world of pharmaceuticals, efficient technology transfer processes are crucial for the successful development, production, and commercialization of drugs. In this blog article, we will explore various strategies and best practices for optimizing these processes, ensuring smooth transitions and minimizing risks.
In the fast-paced world of pharmaceuticals, efficient technology transfer processes are crucial for the successful development, production, and commercialization of drugs. In this blog article, we will explore various strategies and best practices for optimizing these processes, ensuring smooth transitions and minimizing risks.
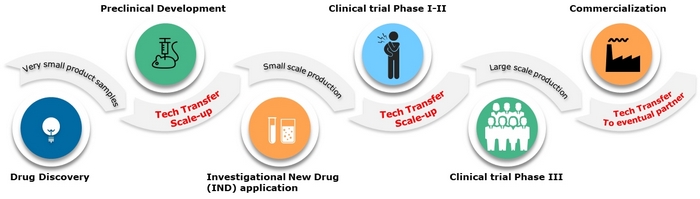
The Importance of Technology Transfer
Technology transfer refers to the movement of knowledge and capabilities from one organization or site to another. In the pharmaceutical industry, it plays a vital role in ensuring that drug development and manufacturing processes are effectively transferred from research and development (R&D) to production facilities.
A well-executed technology transfer process can result in several benefits, including reduced time to market, improved product quality, increased manufacturing efficiency, and enhanced regulatory compliance. On the other hand, poor technology transfer can lead to delays, errors, and even product recalls, causing significant financial losses and reputational damage.
Key Challenges in Technology Transfer
- Complexity of Processes: Pharmaceutical technology transfer involves multiple interconnected processes, such as formulation development, process validation, analytical method transfer, and regulatory filings. Coordinating these activities and ensuring seamless communication between teams can be challenging.
- Risk Management: The transfer of processes from one site to another introduces various risks, including equipment and facility compatibility, raw material sourcing, and regulatory compliance. Identifying and mitigating these risks is crucial to ensure a successful transfer.
- Knowledge Transfer: Transferring tacit knowledge and expertise from experienced personnel to the receiving site is essential for maintaining product quality and process efficiency. Capturing and documenting this knowledge is often a complex task.
Best Practices for Optimizing Technology Transfer
- Early Involvement of Cross-Functional Teams: Engaging cross-functional teams from the early stages of technology transfer helps ensure that all relevant stakeholders are involved and aligned. This includes representatives from R&D, manufacturing, quality control, regulatory affairs, and supply chain.
- Comprehensive Risk Assessment: Conducting a thorough risk assessment prior to technology transfer is crucial. This involves identifying potential risks, evaluating their impact, and implementing appropriate mitigation strategies. Regular risk reviews should also be conducted throughout the transfer process.
- Standardization of Documentation: Establishing standardized documentation processes and templates for technology transfer can help streamline communication and ensure consistency across sites. This includes protocols, batch records, standard operating procedures (SOPs), and quality control specifications.
- Effective Communication and Training: Clear and effective communication between the sending and receiving sites is essential. This includes regular meetings, progress updates, and training sessions to transfer knowledge and ensure a shared understanding of processes and requirements.
- Continuous Improvement and Lessons Learned: Technology transfer is an iterative process, and continuous improvement is key. Regularly reviewing and analyzing transfer performance, capturing lessons learned, and implementing corrective actions are essential for ongoing optimization.
Conclusion
Optimizing pharma tech transfer services processes is vital for the successful development and commercialization of drugs. By following best practices such as early involvement of cross-functional teams, comprehensive risk assessment, standardization of documentation, effective communication and training, and continuous improvement, organizations can minimize risks, enhance efficiency, and ensure the seamless transfer of knowledge and capabilities.
